Process (How)
In the context of innovation, the process aspect refers to the complete innovation process—from idea generation, prototyping, a system for project selection, R and D cost control, speed to market, piloting, test methodology, ramp-up mechanism, and risk assessment to analyzing and handling market regulations and management of the complete product life cycle. Typically, the innovation process is linked and adopted depending on the innovation horizon and the company’s mix in the innovation portfolio. This aspect is linked strongly to profit and is both internally and externally focused.
Organization
Here, the term “organization” is used to describe the organization’s ability to deliver innovation projects. Capabilities that are especially important to this aspect are engaging and involving people, supporting goal-oriented leadership with a clear vision, and setting a high priority on innovation in all horizons. Idea diffusion within the organization and cross-functional capabilities, together with talent management and reward systems for innovations, are especially important. This aspect is internal and typically drives profit.
Learning Capabilities
Learning is essential to innovation on several levels. Critical capabilities like being opportunistic, involving C-level management, running cross-disciplinary learning, evaluation, and a reward system are essential. Gaining insight from the horizon tree is especially crucial to succeeding in horizons one and two. Well-known large corporations operating in all three horizons and rewarded for their learning efforts include IBM, MindTree, and Verizon. In general, learning is an internal activity and is highly linked to profitability.
Supply
Supply development concerns scanning and involving suppliers and partners in order to extend the core business that you are really good at. Typically, today’s organizations go about this by defining new digital solutions, new business models, and new ways of producing and delivering offers to the market through digital trading places. The supply-innovation aspect is internal and strongly linked to profit.
Channel (Where)
The channel aspect is one of the most important to finding new ways of building the capability to interact with the outside world. It is also one of the hardest to expand and develop, as it is not obvious during the emerging phase. Channel development is about how the offer is consumed, how it is distributed, and its delivery format. But to succeed, new channels cannot just add distribution; they also have to find new ways of consuming the products or services, maybe by adding machine learning or through new technical formats.
Linkages
The linkages aspect is a broad concept that encompasses building and utilizing so-called “eco-systems” for developing, engaging, and rewarding external parties, benchmarking, reverse-engineering existing solutions, watching and learning about new technology in order to be faster, increasing capacity, and ultimately mitigating risks to keep the speed-to-market rate high. This kind of multifaceted eco-system is one of the most efficient ways of working in parallel in all three horizons, from incremental innovation to radical technology-driven innovations, even with scarce resources. Linkages increase the size of a company’s reachable market and are built upon internal strength in identifying, collaborating, and exchanging innovations with outside parties.
Openness
Openness is not about being uncommercial; it is about setting the stage for creating together, learning together, and eventually protecting IP together through patent exchange. The openness aspect typically contributes to growth of the market and is based on internal changes and development of capabilities for opening up and sharing.
Brand
The aspect “brand” addresses the activities of generating demand, sharing through telling, and setting the stage for creating so-called diffusion of new innovations. This aspect is also used well by the experience industries, such as resorts, movies, gaming, and the music business. It is used for generating and growing the market and is built upon primarily internal activities and capabilities.
 The innovation capability of your organization is not simply the ability to generate new ideas or create new products. It is the holistic, comprehensive, and all encompassing ability of your entire organization to respond to changes in the business environment with actions that deliver real value to the organization.
The innovation capability of your organization is not simply the ability to generate new ideas or create new products. It is the holistic, comprehensive, and all encompassing ability of your entire organization to respond to changes in the business environment with actions that deliver real value to the organization. 
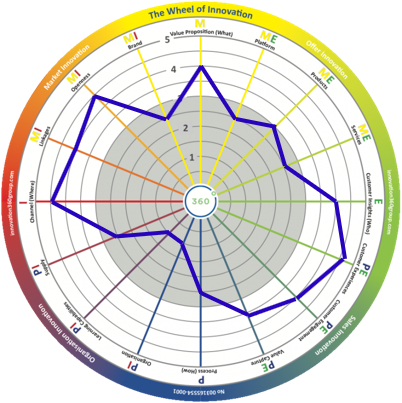
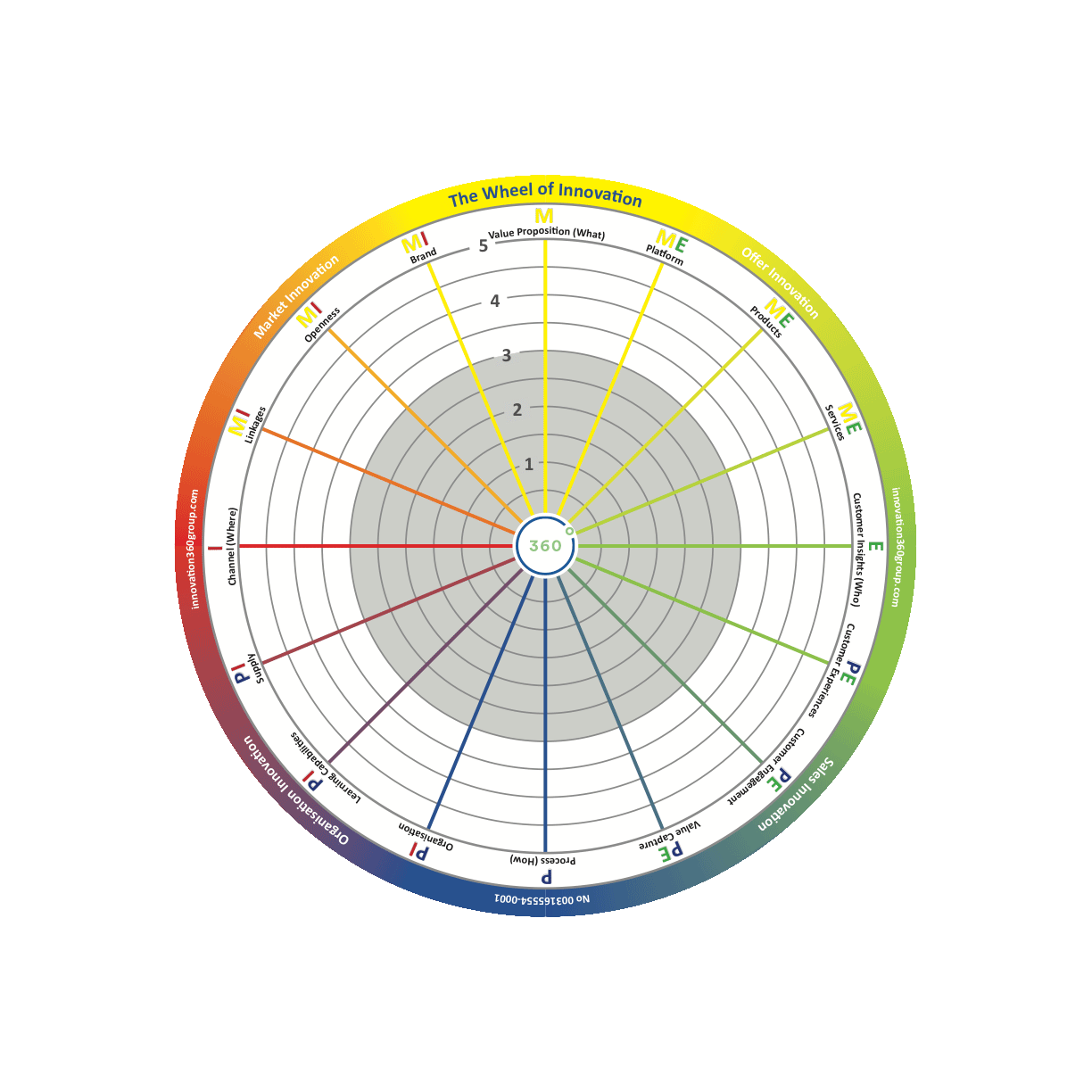
 The right side of the wheel is about external innovation which is focused on how to organize for efficient customization of market deliverables. This includes designing intelligent building platforms able to deliver customized products and services together with understanding how to create a superior customer engagement and experience.
The right side of the wheel is about external innovation which is focused on how to organize for efficient customization of market deliverables. This includes designing intelligent building platforms able to deliver customized products and services together with understanding how to create a superior customer engagement and experience.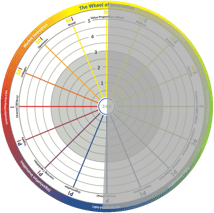 The left side of the wheel is about how to organize for knowledge creation and sharing, production, process development and redesign, supply and cross-border learning. Artificial intelligence will most likely be a driving force in the development of internal innovation over the coming years.
The left side of the wheel is about how to organize for knowledge creation and sharing, production, process development and redesign, supply and cross-border learning. Artificial intelligence will most likely be a driving force in the development of internal innovation over the coming years.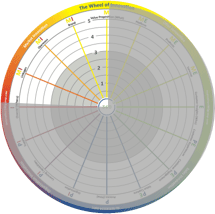 The upper left quadrant (MI) is where market innovation takes place. Typically, this is where you use external resources in an open co-creation process to achieve a larger accessible market through building value nets and growing the total market. An example is Tesla and how Elon Musk gave away patents to grow the electrical car market instead of fighting against all car manufacturers and eventually ending up in a declining and/or price-pressured market. This quadrant is next to "offer innovation" (see below) and "organizational innovation" (see below) and there is an interaction between those actions.
The upper left quadrant (MI) is where market innovation takes place. Typically, this is where you use external resources in an open co-creation process to achieve a larger accessible market through building value nets and growing the total market. An example is Tesla and how Elon Musk gave away patents to grow the electrical car market instead of fighting against all car manufacturers and eventually ending up in a declining and/or price-pressured market. This quadrant is next to "offer innovation" (see below) and "organizational innovation" (see below) and there is an interaction between those actions.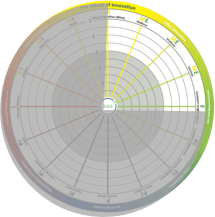 The upper right quadrant is where offer innovation takes place. It is typically based on sales innovation (see below) and market innovation. There will be a structured innovation process for products and services organized in platforms for product or service lifetime management and product or service document management. Examples are all the companies with a structured new product development (NPD) process. Superior companies are often found in, for instance, the fast moving consumer goods (FMCG) and consumer electronics industries.
The upper right quadrant is where offer innovation takes place. It is typically based on sales innovation (see below) and market innovation. There will be a structured innovation process for products and services organized in platforms for product or service lifetime management and product or service document management. Examples are all the companies with a structured new product development (NPD) process. Superior companies are often found in, for instance, the fast moving consumer goods (FMCG) and consumer electronics industries.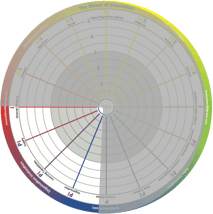 The lower left quadrant is where organizational innovation takes place. Typically, professional services firms (PSFs), and high-tech and pharmaceutical companies put a lot of effort into this area, creating superior structural capital and knowledge processes and a nest of suppliers. This quadrant is next to sales innovation (see below) and market innovation, making it possible to develop the market and sales.
The lower left quadrant is where organizational innovation takes place. Typically, professional services firms (PSFs), and high-tech and pharmaceutical companies put a lot of effort into this area, creating superior structural capital and knowledge processes and a nest of suppliers. This quadrant is next to sales innovation (see below) and market innovation, making it possible to develop the market and sales.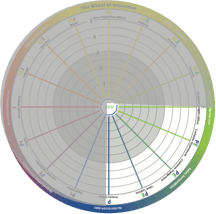 The lower right quadrant is where sales innovation takes place. Typically, it is where you create something new and exciting based on customer insights. This drives sales and loyalty, generating recurring revenue and high lifetime value. One very good example is the App Store in Apple, which creates superior experiences and is constantly used to understand patterns and behavior at the same time as dragging you into an echo system that is hard to leave. Sales innovation is based on the work of organizational innovation and offer innovation, but it is centered around the experience and engagement itself.
The lower right quadrant is where sales innovation takes place. Typically, it is where you create something new and exciting based on customer insights. This drives sales and loyalty, generating recurring revenue and high lifetime value. One very good example is the App Store in Apple, which creates superior experiences and is constantly used to understand patterns and behavior at the same time as dragging you into an echo system that is hard to leave. Sales innovation is based on the work of organizational innovation and offer innovation, but it is centered around the experience and engagement itself.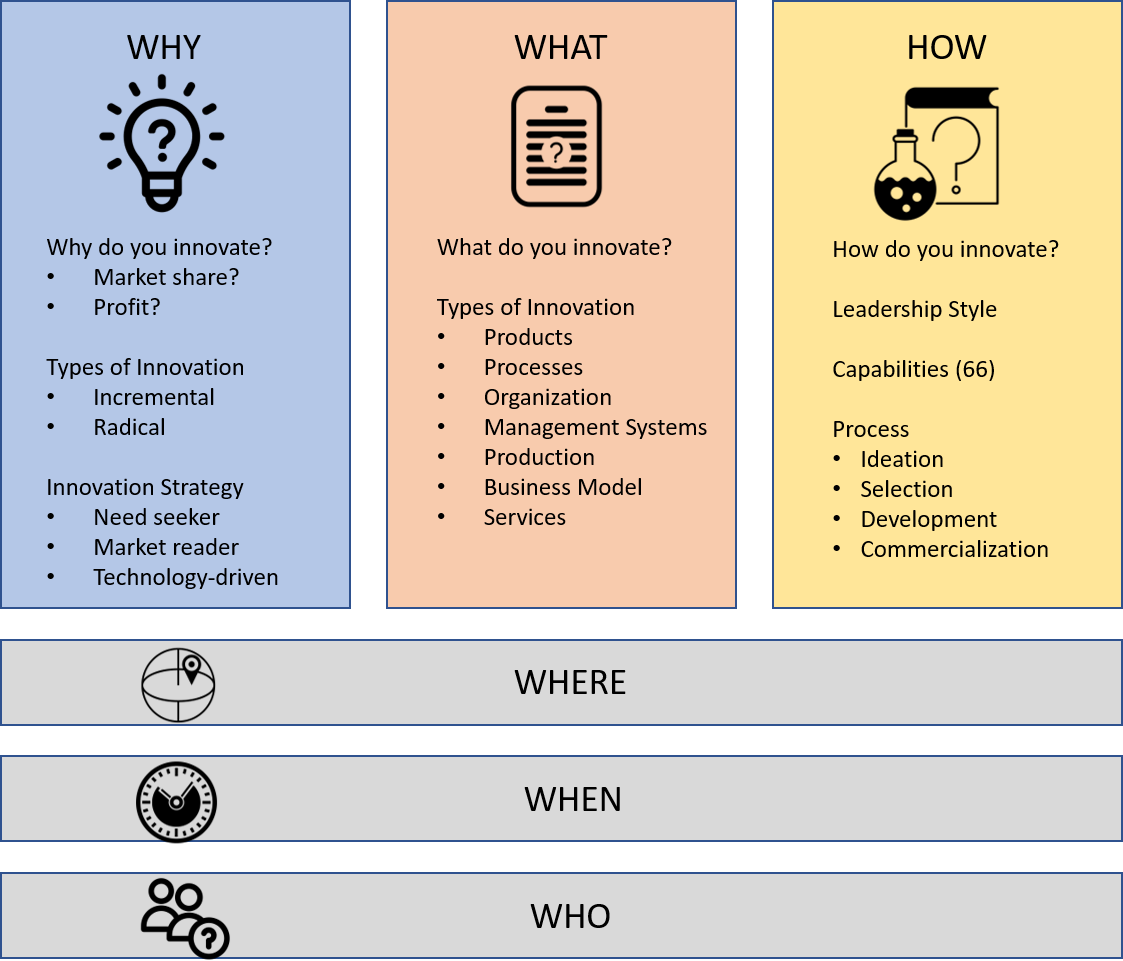






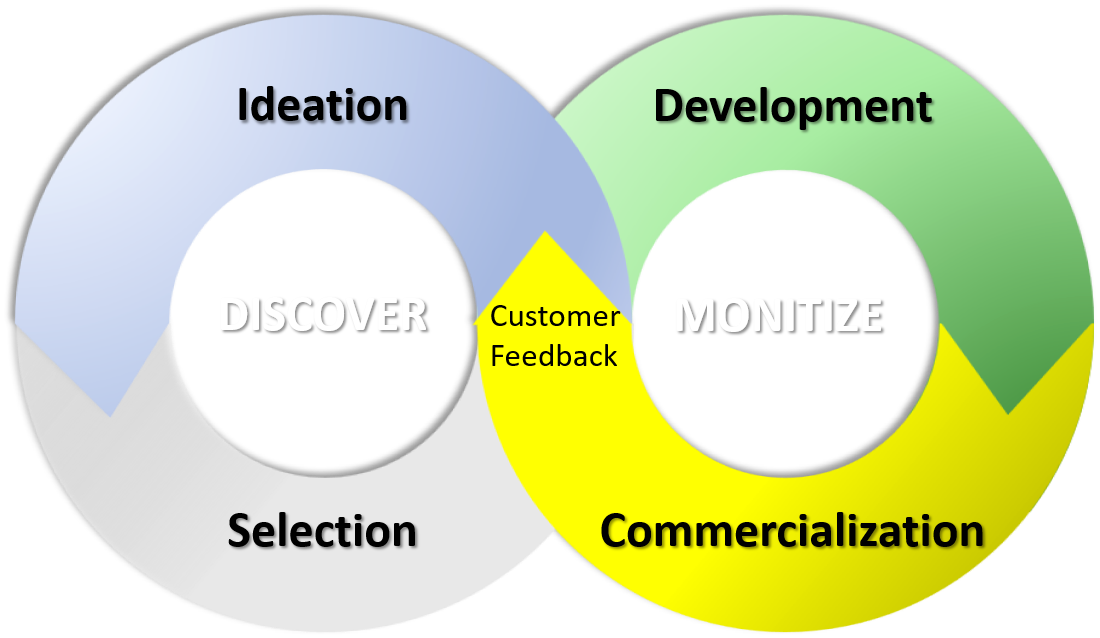
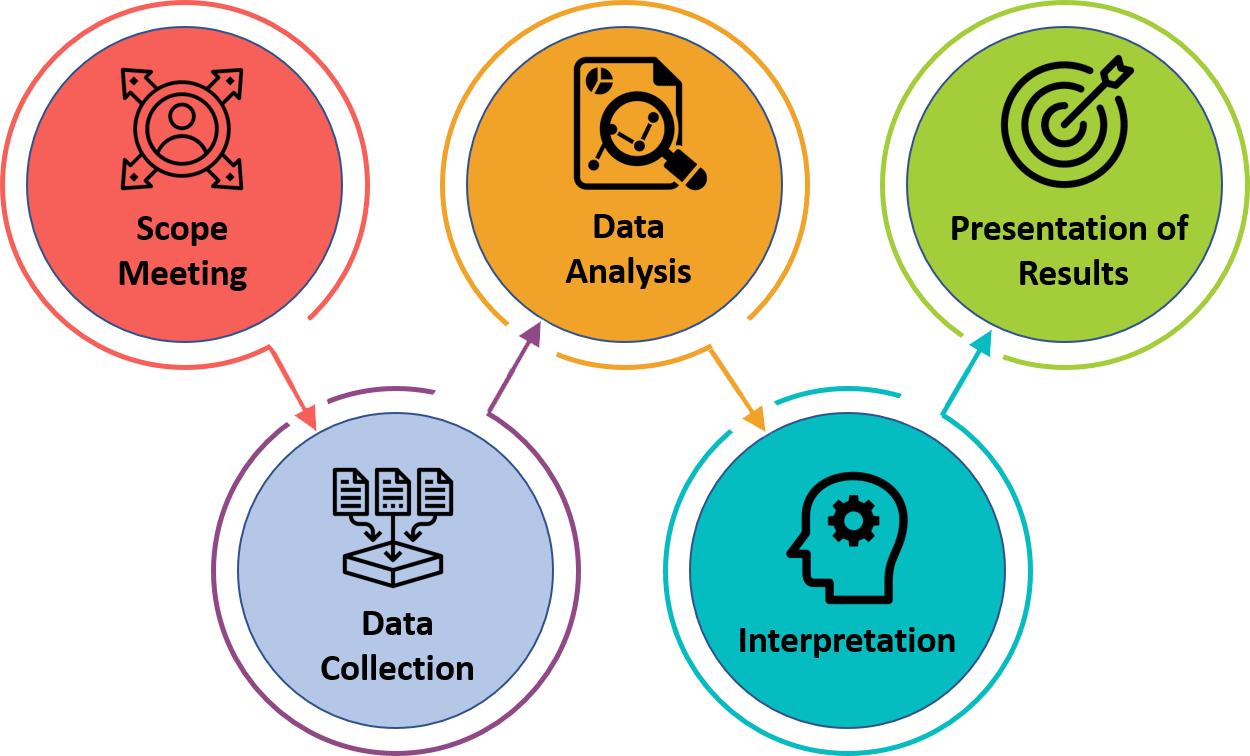
 Our innovation capability consulting and advisory services are grounded in three offerings.
Our innovation capability consulting and advisory services are grounded in three offerings. today (281.858.3271) for a free no obligation discussion of your current needs and situation.
today (281.858.3271) for a free no obligation discussion of your current needs and situation.