Lenses of Innovation
The arrangement of the 16 organizational aspects on the Wheel of InnovationTM (from Innovation360) are deliberately structured to provide 8 different lenses on the innovation capabilities of the organization. The wheel is divided into quadrants defined by a horizontal axis defined by a focus on internal vs. external transformation, forming the left and right hemispheres. The vertical axis define the focus on profit vs. market share which form the top and bottom hemispheres. The quadrants then align with four types of innovation: market, offer, sales, and organization.
 The right side of the wheel is about external innovation which is focused on how to organize for efficient customization of market deliverables. This includes designing intelligent building platforms able to deliver customized products and services together with understanding how to create a superior customer engagement and experience.
The right side of the wheel is about external innovation which is focused on how to organize for efficient customization of market deliverables. This includes designing intelligent building platforms able to deliver customized products and services together with understanding how to create a superior customer engagement and experience. The left side of the wheel is about how to organize for knowledge creation and sharing, production, process development and redesign, supply and cross-border learning. Artificial intelligence will most likely be a driving force in the development of internal innovation over the coming years.
The left side of the wheel is about how to organize for knowledge creation and sharing, production, process development and redesign, supply and cross-border learning. Artificial intelligence will most likely be a driving force in the development of internal innovation over the coming years. The upper left quadrant (MI) is where market innovation takes place. Typically, this is where you use external resources in an open co-creation process to achieve a larger accessible market through building value nets and growing the total market. An example is Tesla and how Elon Musk gave away patents to grow the electrical car market instead of fighting against all car manufacturers and eventually ending up in a declining and/or price-pressured market. This quadrant is next to "offer innovation" (see below) and "organizational innovation" (see below) and there is an interaction between those actions.
The upper left quadrant (MI) is where market innovation takes place. Typically, this is where you use external resources in an open co-creation process to achieve a larger accessible market through building value nets and growing the total market. An example is Tesla and how Elon Musk gave away patents to grow the electrical car market instead of fighting against all car manufacturers and eventually ending up in a declining and/or price-pressured market. This quadrant is next to "offer innovation" (see below) and "organizational innovation" (see below) and there is an interaction between those actions.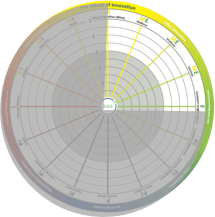 The upper right quadrant is where offer innovation takes place. It is typically based on sales innovation (see below) and market innovation. There will be a structured innovation process for products and services organized in platforms for product or service lifetime management and product or service document management. Examples are all the companies with a structured new product development (NPD) process. Superior companies are often found in, for instance, the fast moving consumer goods (FMCG) and consumer electronics industries.
The upper right quadrant is where offer innovation takes place. It is typically based on sales innovation (see below) and market innovation. There will be a structured innovation process for products and services organized in platforms for product or service lifetime management and product or service document management. Examples are all the companies with a structured new product development (NPD) process. Superior companies are often found in, for instance, the fast moving consumer goods (FMCG) and consumer electronics industries.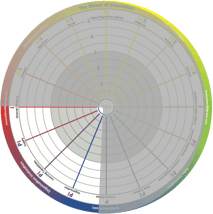 The lower left quadrant is where organizational innovation takes place. Typically, professional services firms (PSFs), and high-tech and pharmaceutical companies put a lot of effort into this area, creating superior structural capital and knowledge processes and a nest of suppliers. This quadrant is next to sales innovation (see below) and market innovation, making it possible to develop the market and sales.
The lower left quadrant is where organizational innovation takes place. Typically, professional services firms (PSFs), and high-tech and pharmaceutical companies put a lot of effort into this area, creating superior structural capital and knowledge processes and a nest of suppliers. This quadrant is next to sales innovation (see below) and market innovation, making it possible to develop the market and sales.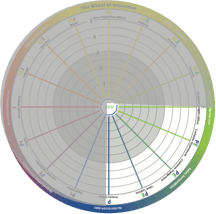 The lower right quadrant is where sales innovation takes place. Typically, it is where you create something new and exciting based on customer insights. This drives sales and loyalty, generating recurring revenue and high lifetime value. One very good example is the App Store in Apple, which creates superior experiences and is constantly used to understand patterns and behavior at the same time as dragging you into an echo system that is hard to leave. Sales innovation is based on the work of organizational innovation and offer innovation, but it is centered around the experience and engagement itself.
The lower right quadrant is where sales innovation takes place. Typically, it is where you create something new and exciting based on customer insights. This drives sales and loyalty, generating recurring revenue and high lifetime value. One very good example is the App Store in Apple, which creates superior experiences and is constantly used to understand patterns and behavior at the same time as dragging you into an echo system that is hard to leave. Sales innovation is based on the work of organizational innovation and offer innovation, but it is centered around the experience and engagement itself.
 today (281.858.3271) for a free no obligation discussion of your current needs and situation.
today (281.858.3271) for a free no obligation discussion of your current needs and situation.